Topic 11
INTRODUCTION
TO ORGANIC COMPOUND
WHAT IS THE ORGANIC CHEMISTRY?
- Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon compond.
- Organic compound contain H as well C, while other elements are O, N, the halogens, S and P
- They may exist as simple or complex molecules, as gases, liquids or solid and coloured or colourless.
The
physical and chemical properties of organic compounds depends on two factors:
- The number and arrangement of carbon atoms in the molecule:
A number of important physical properties
are determined by the number of carbon atoms in the molecule. The greater the
number of carbon atoms, the larger the Van der Waal’s forces and the higher the
melting points, boiling points and viscosity
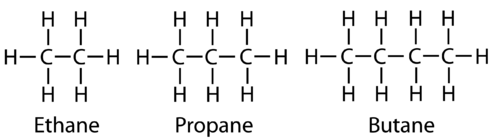
Straight chain.
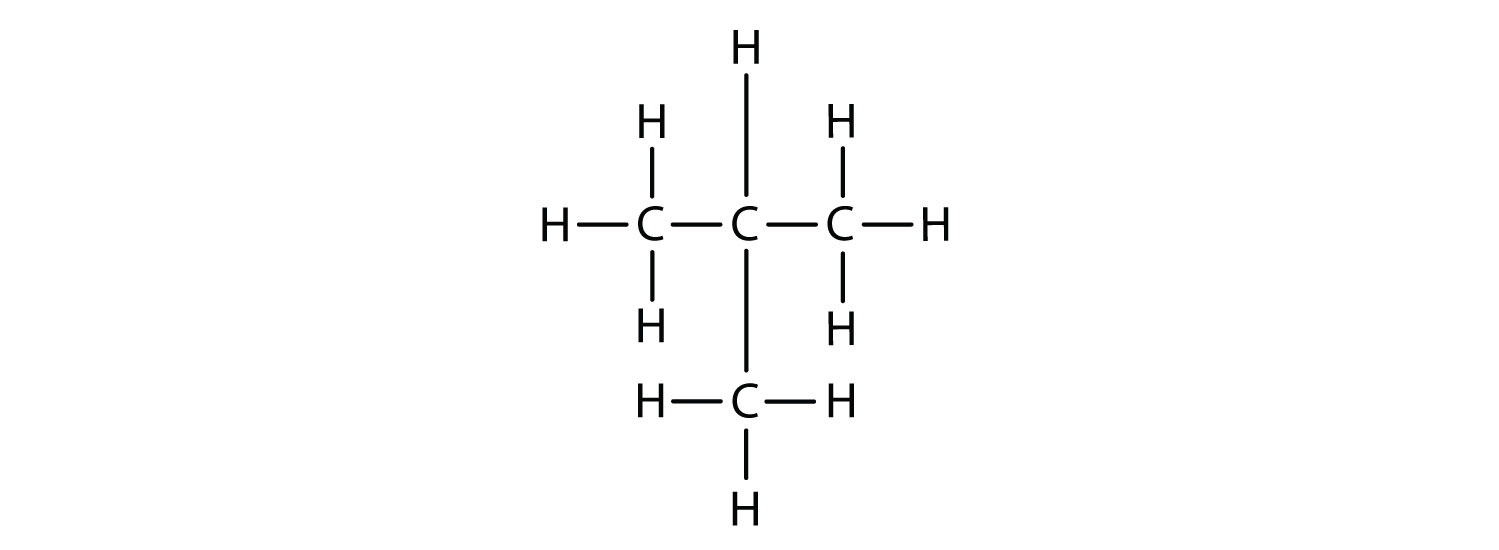
Branched chain.
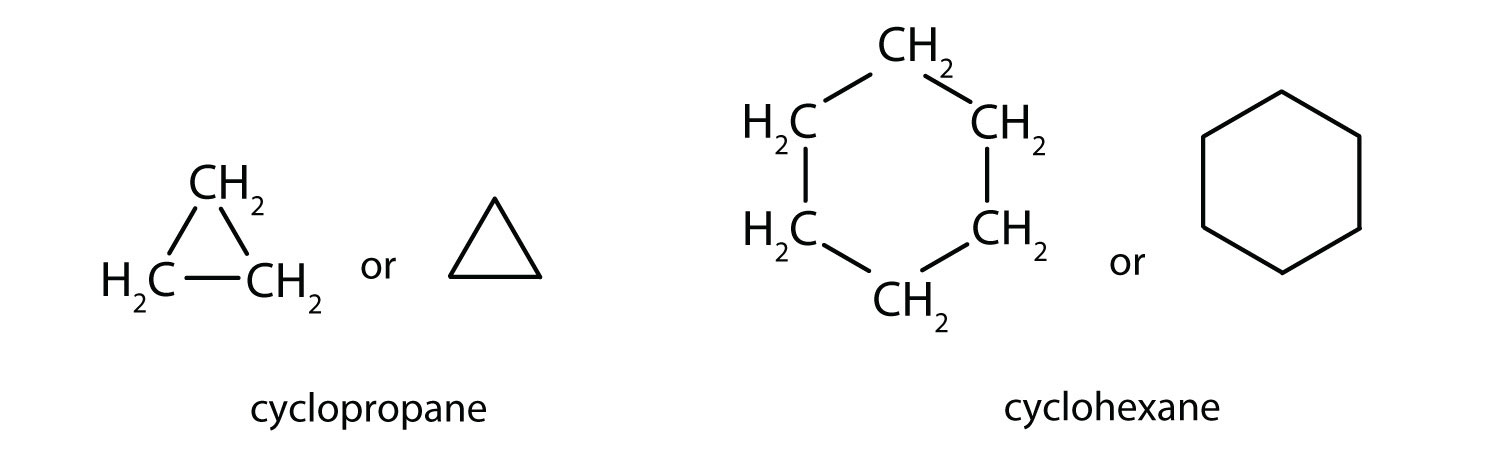
Cyclic Chain
a)
Structural formula is a formula that show how the atoms in a molecules are bonded to each others.
- Show all the covalent bonds between atom.

Condensed structure :
- Does not show single bond between carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- Double and triple are shown.
- If there are 2 or more similar group bonded to the same atom, the condensed structural formula of the group enclosed in brackets and a subscript numeral is used to indicate its number.

Skeletal structure
- Does not shown carbon and hydrogen atom.
- All covalent bond are shown by line.
- Functional groups (as -OH, -CL, -Br) are shown.

3-DIMENSIONAL FORMULA
- Describe how the atoms of a molecules are arranged in space.

CLASSIFICATION OF CARBON AND HYDROGEN ATOM IN ORGANIC MOLECULES.
example:
example:

In other words:
- A primary carbon can be written as 1° (#1 with a degree symbol) has one carbon attached to this carbon atom.
- A secondary carbon written as 2° (#2 with a degree symbol) is a carbon attached to two other carbons.
- A tertiary carbon written as 3° (#3 with a degree symbol) is a carbon attached to three other carbons.
- And a quaternary carbon written as 4° (#4 with a degree symbol) is a carbon attached to four other carbons.
I want you to recognize that the quaternary carbon is attached ONLY to carbon. This is because having four bonds to carbon means that carbon already has its complete octet. But primary, secondary and tertiary carbons will have other atoms attached. These atoms can include hydrogen, halogens (F, Cl, Br, I), oxygen, nitrogen, and so on.
The functional groups
A functional group is an atom or group of atoms in an organic molecule which characterised the molecules and enables it to react in specific ways which determines its chemical properties
Functional groups.
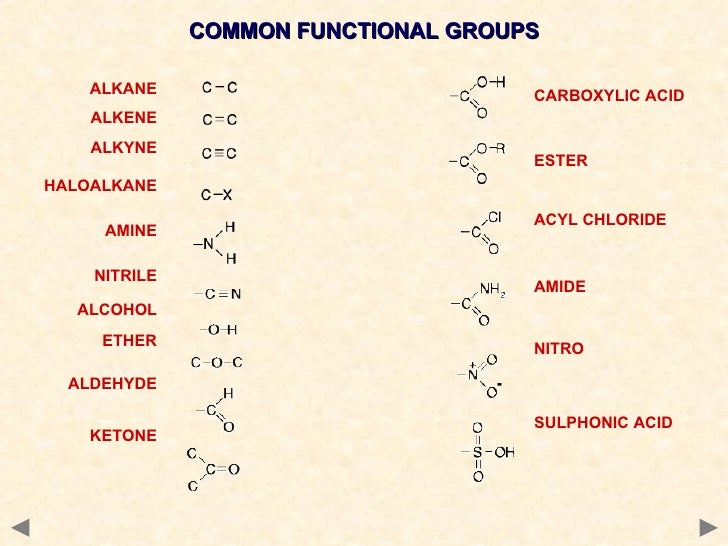
How to remember functional group (easy way).
HOMOLOGS SERIES.
- A group of compounds with the same functional group.
- Obey a general formula. example: alkane, alkene.
- Differ from the successive homolog by a CH2 unit.
- show a gradual change in the pysical properties.
- Have same functional group.
- Have similar chemical properties.
- Can be prepared by similar general methods.
Instant Fact.
- Alkanes and cycloalkanes belong to the class of compound since they have similar functional group. However, they belong to the different homologous series alkanes (CnH2n+2) and cycloalkanes (CnH2n) have different general formula.
